About me
I completed my PhD from the Indian Institute of Technology Palakkad under the guidance of Prof. Chandrashekar Lakshminarayanan (IIT Madras). As a part of my PhD work, we developed novel AI based models and techniques for three foundational problems in personalized learning systems. My thesis contributes to the the problem of teaching a set of related topics, also referred to as a curriculum, to a student through adaptive sequencing of activities and learning resources.
Research interests
- Artificial intelligence for education
- Machine learning
- Educational data mining
PhD research work
CurriculumTutor: a novel tutoring algorithm for mastering a curriculum using adaptive activity sequencing
Won the best paper award at AIED 2022 [Paper]
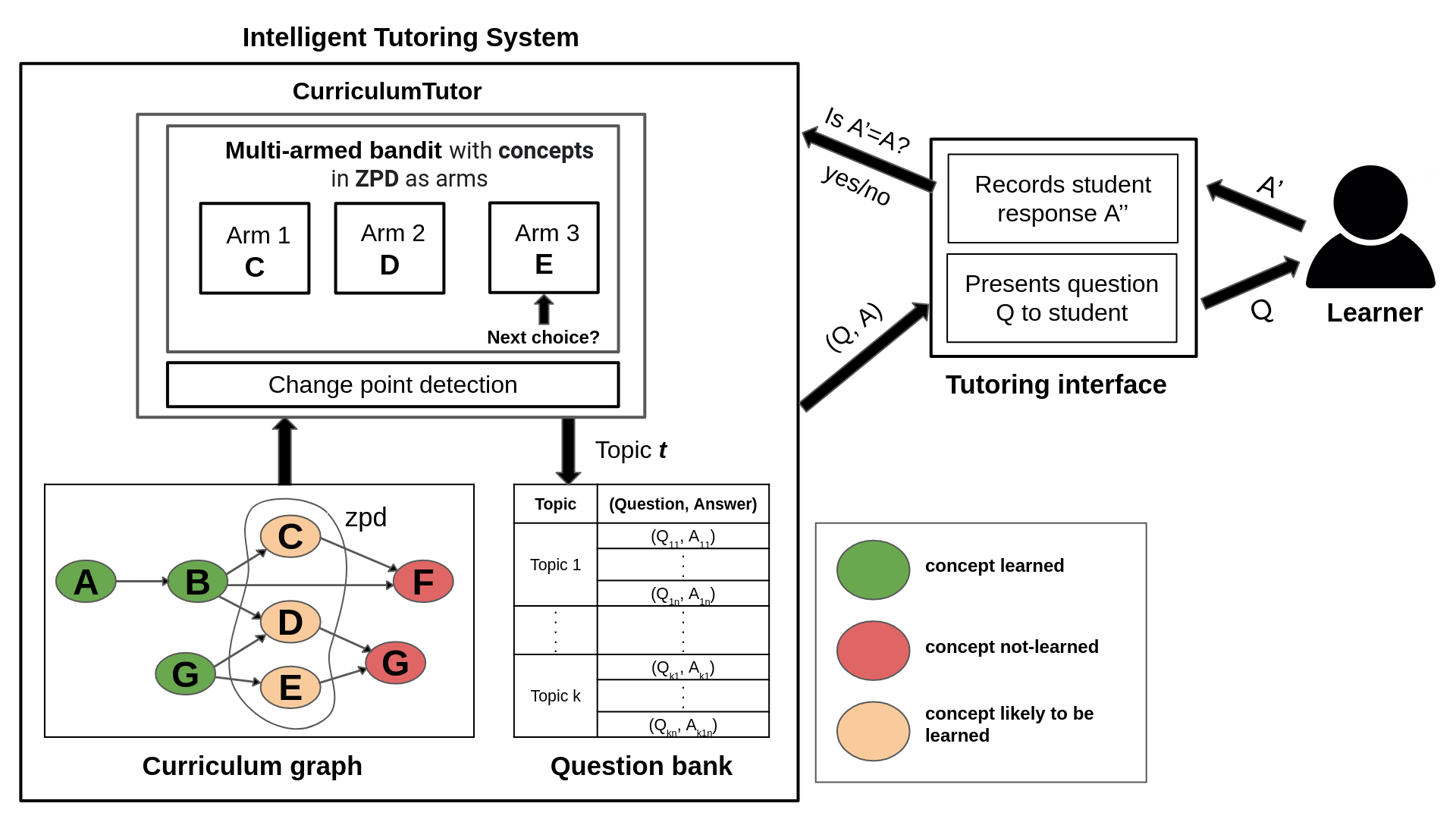
An important problem in an intelligent tutoring system (ITS) is that of adaptive sequencing of learning activities in a personalised manner so as to improve learning gains. In this paper, we consider intelligent tutoring in the learning by doing (LbD) setting, wherein the concepts to be learnt along with their inter-dependencies are available as a curriculum graph, and a given concept is learnt by performing an activity related to that concept (such as solving/answering a problem/question). For this setting, recent works have proposed algorithms based on multi-armed bandits (MAB), where activities are adaptively sequenced using the student response to those activities as a direct feedback. In this paper, we propose CurriculumTutor, a novel technique that combines a MAB algorithm and a change point detection algorithm for the problem of adaptive activity sequencing. Our algorithm improves upon prior MAB algorithms for the LbD setting by (i) providing better learning gains, and (ii) reducing hyper-parameters thereby improving personalisation. We show that our tutoring algorithm significantly outperforms prior approaches in the benchmark domain of two operand addition up to a maximum of four digits.
Unsupervised concept tagging of mathematical questions from student explanations
Presented at AIED 2023 [Paper]
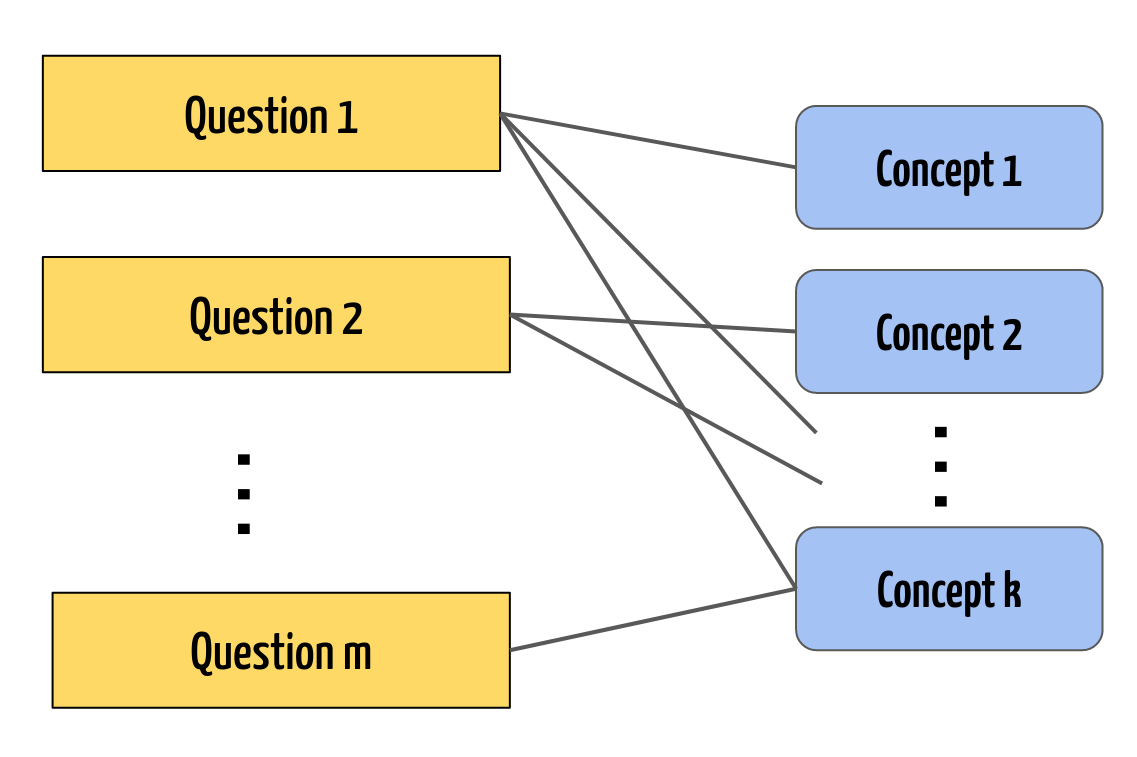
Assigning concept tags to questions enables Intelligent tutoring systems (ITS) to efficiently organize resources, help identify students’ strengths and weaknesses, and recommend suitable learning materials accordingly. Manual tagging is time-consuming, and inefficient for large question banks, and could lead to consistency issues due to differences in the perspectives of individual taggers. Automatic tagging techniques can efficiently generate consistent tags at lower costs. Generating automatic tags for mathematical questions is challenging as the question text is usually short and concise, and the question as well as the answer text contains mathematical symbols and formulas. However, prior works have not studied this problem extensively. In this context, we conducted a study in a graduate-level linear algebra course to understand if student explanations to solving mathematical problems can be employed to generate concept tags associated with those questions. In this work, we propose a method called Unsupervised Skill Tagging (UST) to extract concept tags associated with a given assessment item from explanation text. Using UST on the explanations generated, we show that the explanations indeed contain the expert-specified concept tags.
Content sequencing
Under Review
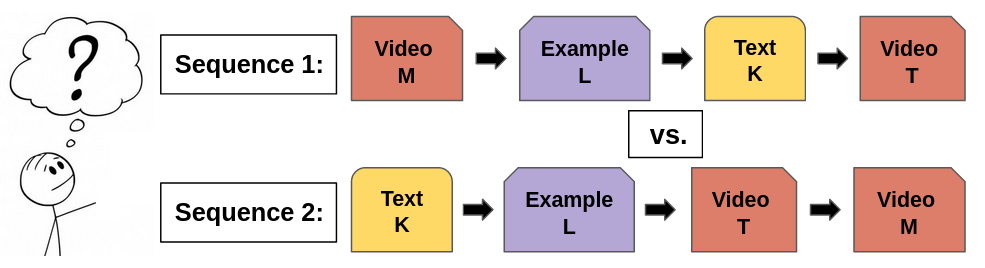
Given a set of resources such as videos, worked out examples, etc. related to a given concept, find an optimal sequence of resources that maximizes the probability of a student mastering the concept within a time horizon H.
Publications
-
Shabana, K. M., Lakshminarayanan, C., & Anil, J. K. (2022). CurriculumTutor: An Adaptive Algorithm for Mastering a Curriculum. In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education (pp. 319-331). Springer, Cham. [Paper] Won the best paper award at AIED 2022: The 23rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education
-
Shabana, K.M., Lakshminarayanan, C. (2023). Unsupervised Concept Tagging of Mathematical Questions from Student Explanations. In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education (pp. 627-638), vol 13916. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland. [Paper]
-
Shabana, K. M., Nazeer, K. A., Pradhan, M., & Palakal, M. (2015). A computational method for drug repositioning using publicly available gene expression data. BMC bioinformatics, 16(17), S5. [Paper] Won the best paper award at IEEE 4th International Conference on Computational Advances in Bio and Medical Sciences (ICCABS), 2014
-
Shabana, K. M., & Wilson, J. (2015, May). A novel method for automatic discovery, annotation and interactive visualization of prominent clusters in mobile subscriber datasets. In 2015 IEEE 9th International Conference on Research Challenges in Information Science (RCIS) (pp. 127-132). IEEE. [Paper]
-
Shabana, K. M., Wilson, J., & Chaudhury, S. (2016, August). A multi-view non-parametric clustering approach to mobile subscriber segmentation. In 2016 IEEE 18th Conference on Business Informatics (CBI) (Vol. 1, pp. 173-181). IEEE. [Paper]
Work experience
-
Research and Development Engineer
Flytxt
(June 2013 - December 2016)Worked on projects related to customer segmentation in telecom domain and developed novel algorithms for performing automatic intelligent grouping of subscribers. Designed interesting visualizations for leveraging value out of large structured/ unstructured data sources, which were later added to the visualization dashboard of the company’s product
Honors and Awards
- Recipient of the prestigious Prime Minister’s Research Fellowship (PMRF)
- Euraxess Science Slam India 2024 Finalist (Top 4)
- Second prize in the Engineering Sciences category of Saransh 2023, a national level competition for thesis presentation in 3 minutes, organized by Indian National Young Academy of Science (INYAS)
- Part of the team that finished second in the Data Challenge held as a part of CODS-COMAD 2024 (11th ACM IKDD CODS and 29th COMAD)
- Best Poster Award in the department of CSE at the Institute Research Scholars‘ Day 2022 in IIT Palakkad
- Winner of the TACT Grand Challenge at CTiS2022, 4th conference on Computational Thinking in Schools, organized by ACM India
- Second prize in Teaching Video Challenge held as a part of Compute 2021
- First prize in Teaching Video Challenge 1 organized by the India Chapter of Special Interest Group on Computer Science Education (iSIGCSE)
- Collaboration Award at Flytxt for demonstrating good team work towards achieving the company’s objectives
- Gold Medal for having scored the highest CGPA in the class for M.Tech Computer Science and Engineering (2013)
- Silver Medal at university level for B.Tech Computer Science and Engineering (2011)
- All India Rank 272 out of 136027 students in the Computer Science and Information Technology paper of the Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering (GATE 2011)
- Ada Lovelace best outgoing girl student award for the year 2010 in Amrita School of Engineering, Amritapuri
- Software Design National Finalist at Microsoft Imagine Cup 2009
Patent
- Systems and methods for management of multi-perspective customer segments US Patent 10,936,620, 2021 (First inventor)
Teaching experience
-
Chief resource person for Internzone - Introduction to Machine Learning
IEEE Kerala Section
(August 2021 - February 2022)Conducted weekly one-hour online sessions on basic machine learning algorithms for third and final year undergraduate engineering students from various colleges in Kerala. Designed and delivered the course content as well as prepared weekly quizzes and programming assignments. [Slides][Recordings]
-
Introduction to Python programming, LaTeX
Government Polytechnic College, Palakkad
(May 2022 - May 2023)Conducted weekly 1-2 hour hands-on sessions on python programming and LaTeX for final year Diploma students of the Computer Hardware Engineering department.
Teaching Assistantship
- Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (2020, 2021), Data Structures and Algorithms Laboratory (2020) and Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (2023): Helped conduct the weekly lab sessions and evaluate student submissions.
- Game Theory and Mechanism Design (2022): Helped evaluate assignments and exam scripts.
- Technical Writing (2023): Prepared the lesson plan, course materials and assignments for the sessions on Introduction to LaTeX and Beamer for first year post-graduate students in the department of CSE. Also conducted the sessions and evaluated the assignments submitted by the students.
- Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (2024): As the Head TA for the course, coordinated a team of 7 TAs in evaluating the submissions made by around 75 undergraduate students for 6 lab assignments. Also prepared the lab assignment on Decision Trees.
Service
- Chaired the session Curriculum and Instruction at AIED 2022
- Chief coordinator of the Computer Science and Engineering (CSE) Research Symposium 2023, IIT Palakkad
- Department coordinator of the Institute Research Scholars Day 2022, IIT Palakkad
Education
- PhD: Indian Institute of Technology Palakkad (2019 - 2025 )
- M.Tech: National Insititue of Technology Calicut (2011 - 2013)
- B.Tech: Amrita School of Engineering, Kollam (2007 - 2011)
Contact
shabana [dot] meethian [at] gmail [dot] com